Introduction
The United States Department of Justice has released a limited and heavily redacted set of documents related to the late financier and convicted sex offender Jeffrey Epstein. The disclosure follows a congressional order demanding transparency but has already drawn criticism for falling short of lawmakers’ expectations.
Partial Disclosure Raises Concerns
The document release, made public on Friday, includes only a small portion of the records held by federal authorities. Several members of the US Congress have expressed concern that the Justice Department did not fully comply with the requirement to release all relevant, non-classified materials connected to Epstein’s investigations.
Officials cited the need to protect:
- Victim identities
- Ongoing legal sensitivities
- Privacy and security concerns
However, critics argue that the level of redaction limits meaningful public understanding.
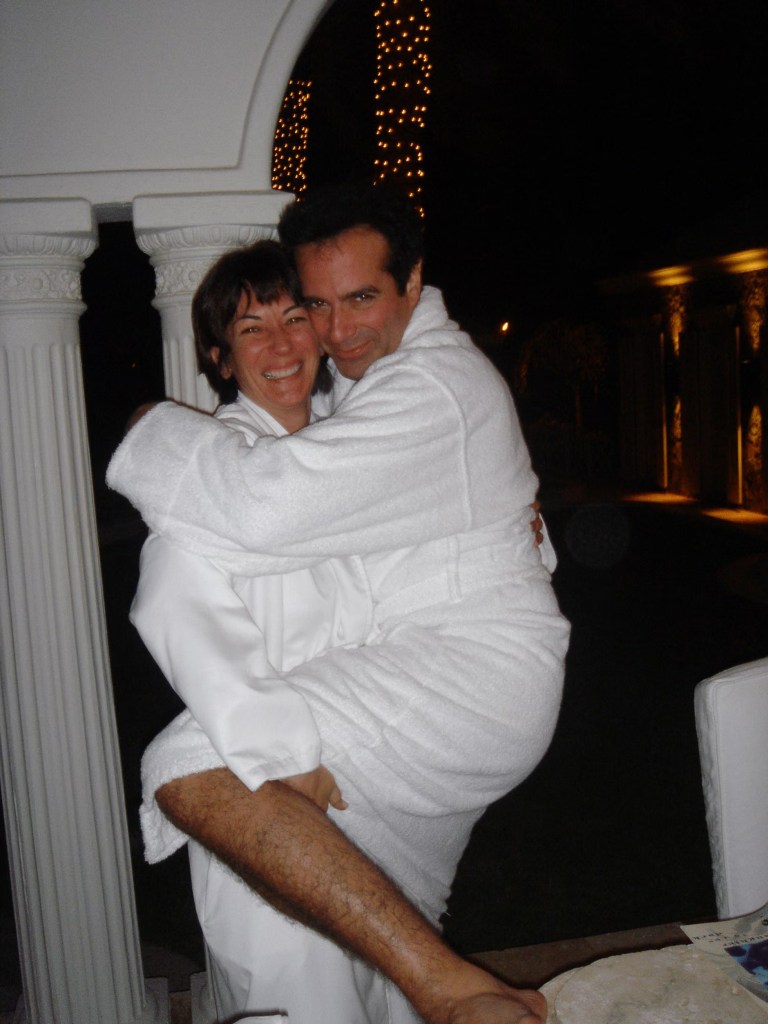
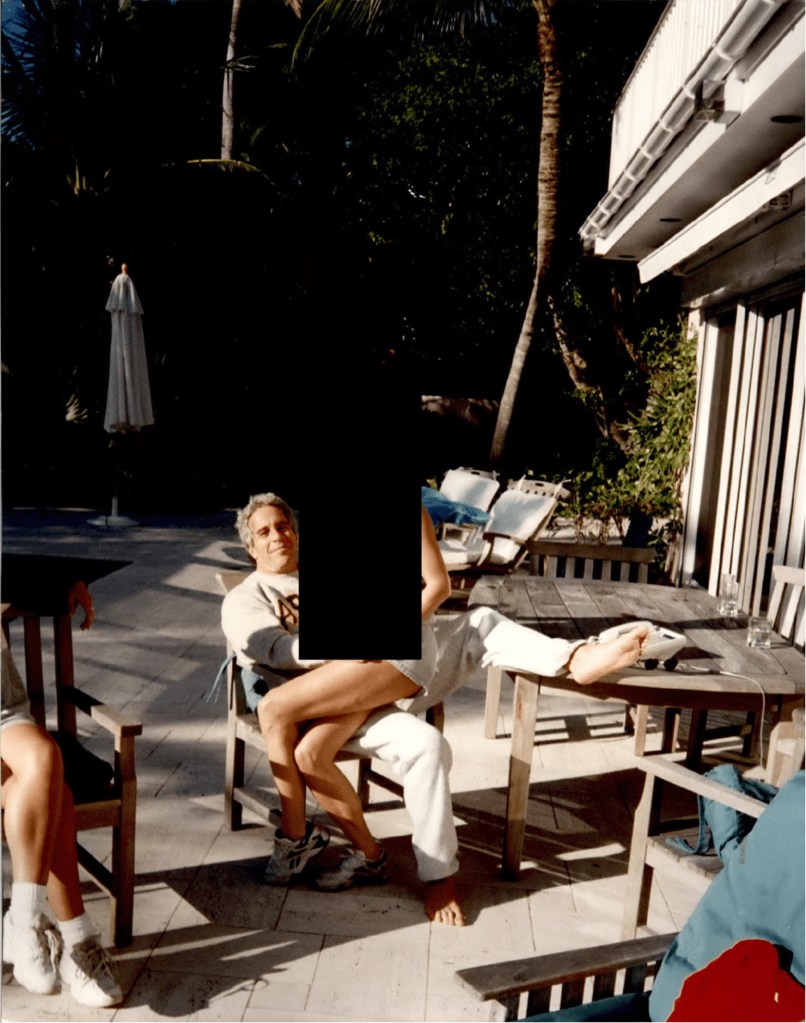
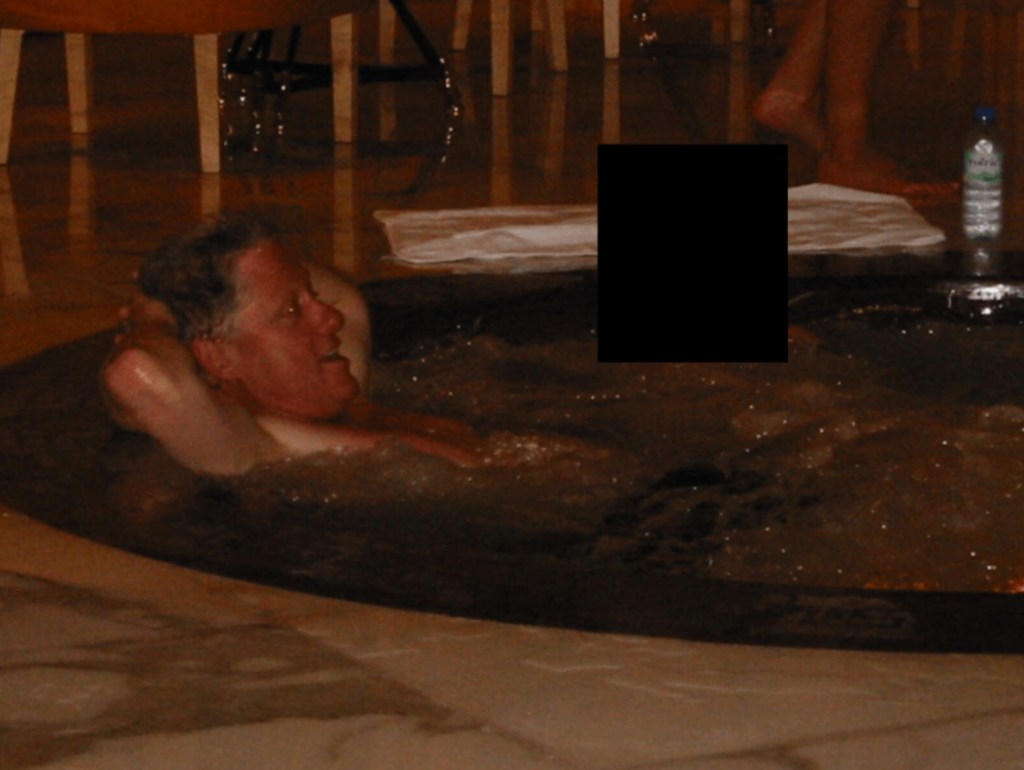



Contents of the Released Documents
The files made public contain:
- Photographs
- FBI interview testimony
- Evidence materials collected during investigations
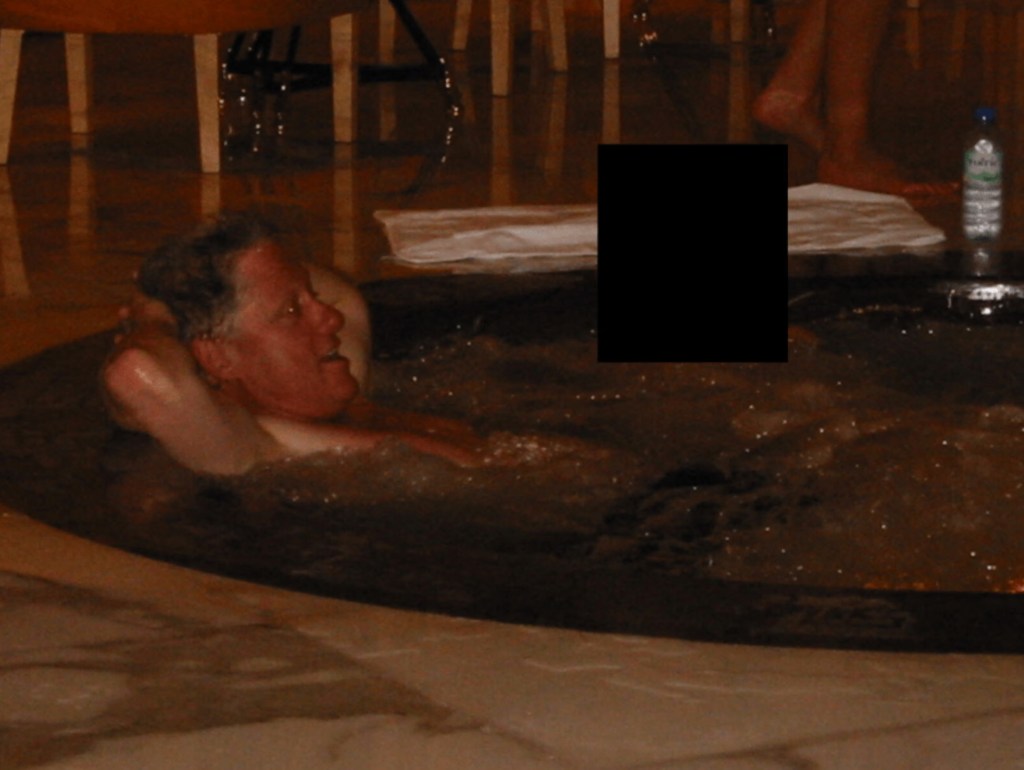
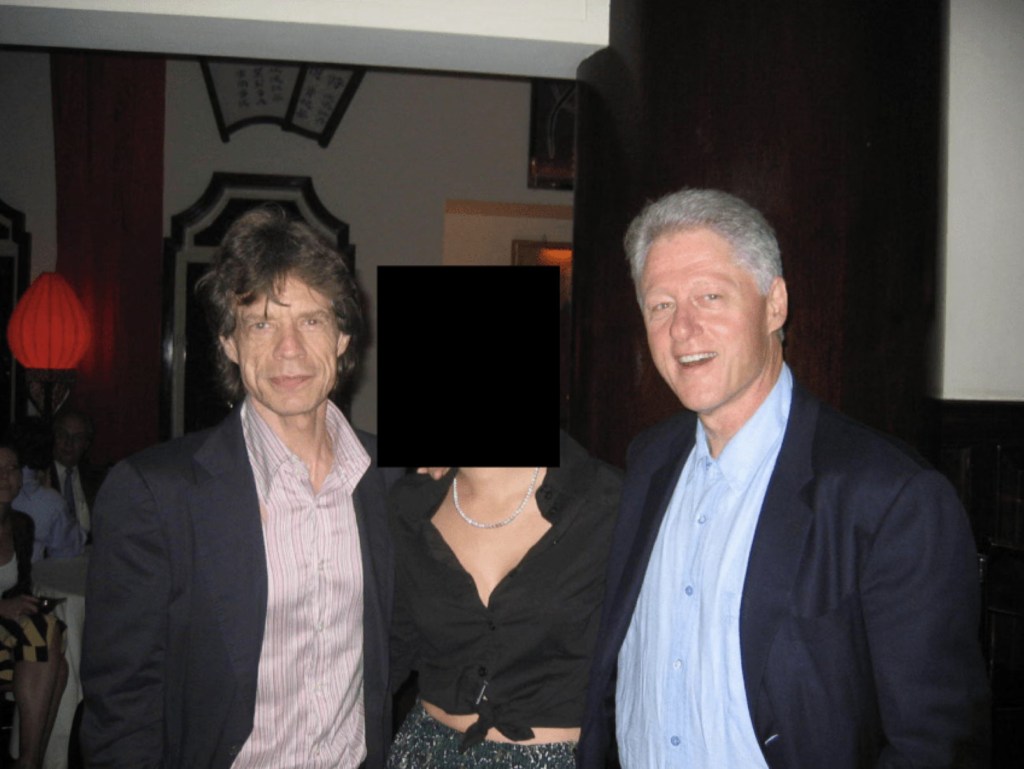
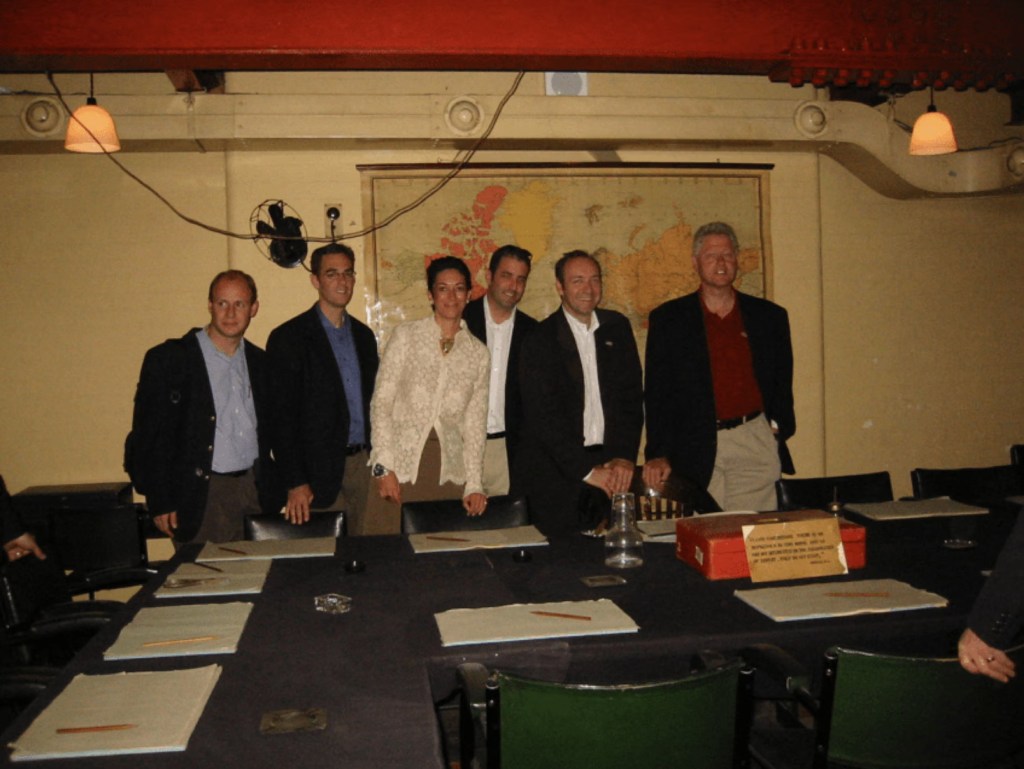
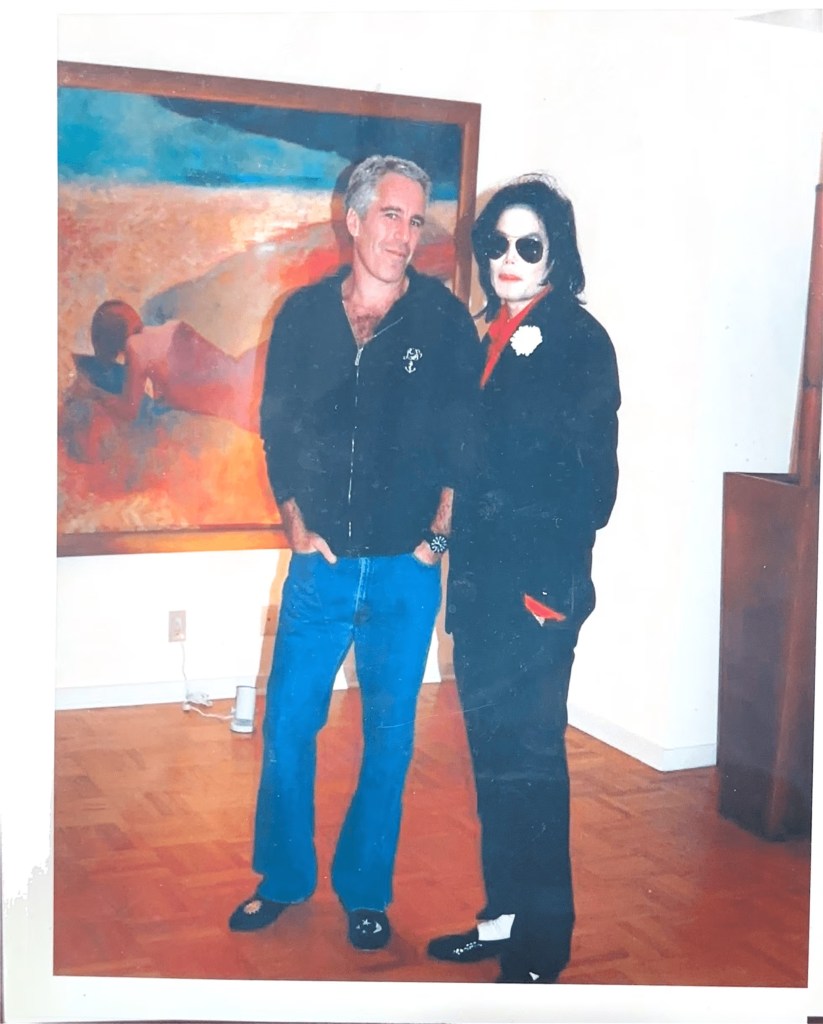
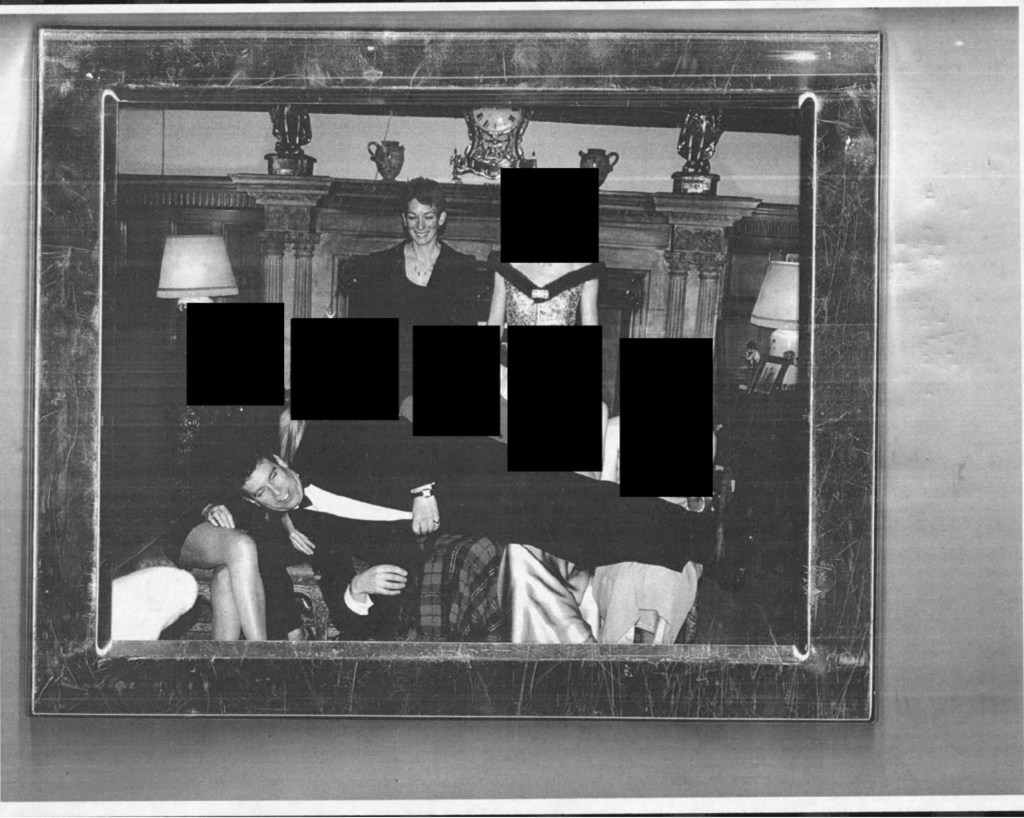
Some images reportedly show Epstein’s residence, including a desk displaying framed photographs of Epstein with well-known public figures.
Among the individuals visible in the released materials are:
- Bill Clinton
- Prince Andrew
- Richard Branson
- Donald Trump
- Pope John Paul II
One image reportedly shows a photograph of Donald Trump stored inside a desk drawer, while others show framed pictures of Epstein with prominent figures placed openly on display.
Important Legal Clarification
Authorities and legal experts have emphasized an important point:
The presence of a person’s image or name in these documents does not imply criminal wrongdoing.
Many of the references reflect:
- Social interactions
- Public events
- Testimony context
No new criminal allegations against the individuals named have been announced as a result of this release.

Congressional Reaction
Several lawmakers have criticized the Justice Department’s approach, arguing that:
- The release does not meet the spirit of congressional oversight
- Excessive redactions undermine transparency
- Public trust depends on fuller disclosure
Some members of Congress have indicated they may seek further clarification or enforcement actions to compel additional releases.
Broader Context of the Epstein Case
Jeffrey Epstein died in federal custody in 2019 while awaiting trial on sex-trafficking charges. Since then:
- Criminal proceedings against him ended
- Civil lawsuits by victims have continued
- Public pressure for transparency has remained strong
The handling of Epstein’s earlier prosecution and plea agreements continues to be examined as a potential example of systemic failure in dealing with powerful offenders.
What Happens Next?
The Justice Department has not ruled out future releases, but has not committed to a clear timeline. Lawmakers and advocacy groups are expected to:
- Continue pressing for full compliance
- Review the released materials
- Push for reforms related to trafficking investigations
Conclusion
The latest release of Epstein-related documents has renewed debate over government transparency, accountability, and the balance between disclosure and privacy. While the files provide limited insight, they have once again placed pressure on authorities to explain how Epstein’s crimes were handled—and whether all relevant facts will eventually be made public.
Disclaimer
This article is based on verified reporting and publicly released information. Mention of individuals does not imply guilt or criminal conduct unless established by a court of law